We've Launched a New Documentation Website (Beta Launch)
The documentation for DuitNow is now available on our newly launched documentation platform. This is an initial beta rollout of our new documentation site, designed to become the long-term home for all documentation moving forward.
You'll find the familiar content you're used to—now hosted on a new platform that will progressively receive updates and enhancements.
We encourage you to start accessing DuitNow materials there to explore the new experience and ensure you're viewing the latest documentation updates. If you have any feedback, please reach out to us.
Visit the New Documentation WebsiteNational Addressing Database (NAD)
National Addressing Database
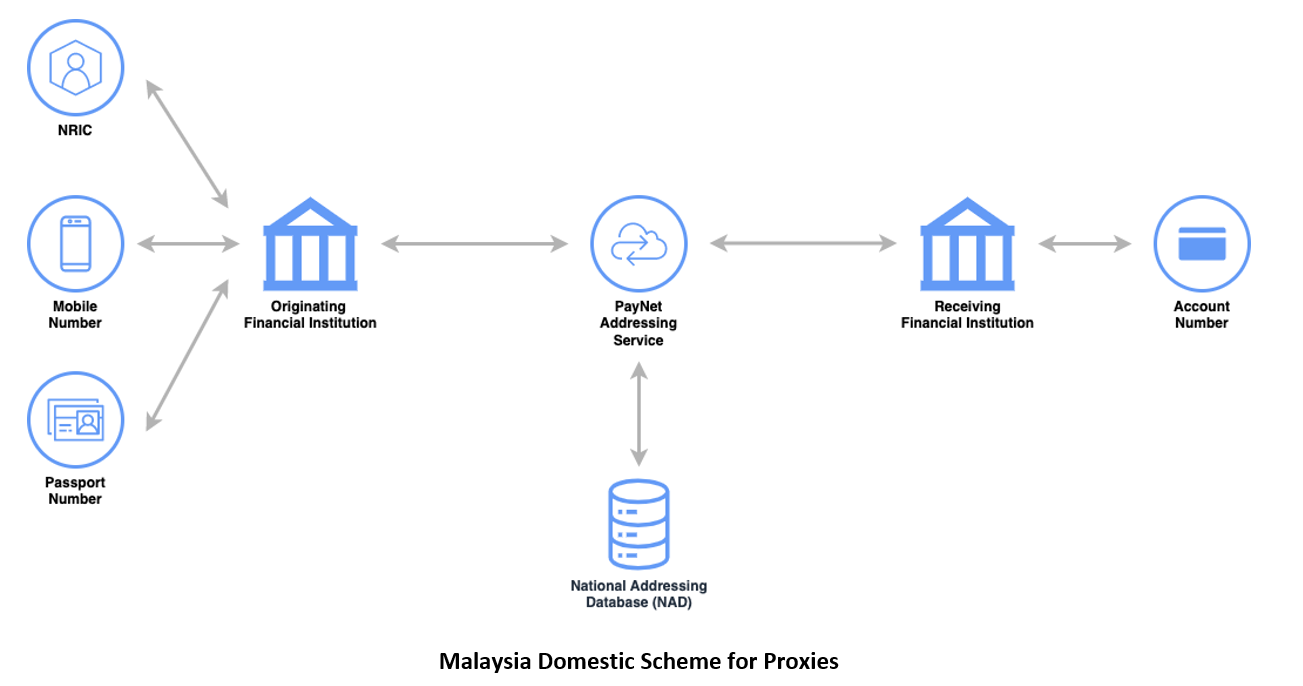
The National Addressing Database (NAD) allows customers to register and link their accounts to a proxy of their choosing. Fundamentally, a unique proxy may be registered and linked to one account which is a one-to-one relationship. However, an account can be linked to multiple proxies which is a one-to-many relationship. These proxy rules apply even when the customer has accounts with multiple Participants.
Over the past years, proxy identifiers have become an integral part especially in countries adopting real-time payment and it is expected to become widespread across the payments landscape.
What is a Secondary Identifier or Proxy?
Traditionally, countries use the Bank Account Number, or IBAN for international payments, as the unique identifier for transactions between banks, serving as a customer’s primary identifier with their financial institution. Proxy or secondary identifiers, like mobile phone numbers, NRIC, or passport numbers, allow customers to make payments by identifying beneficiaries without using account numbers. These proxies are linked to primary identifiers, enabling payment originators to address payments using these convenient, non-account number identifiers.
Enquiry by Secondary ID allows retrieval of all registered aliases linked to a Customer’s Secondary ID within NAD. This enables customers to view all their registered proxies in RPP and allows participants to let customers select which proxy to modify, deregister, suspend, or activate.
Participants can only permit customers to update proxies registered to them. For proxies registered with another participant, customers are only able to view and transfer the proxy to the current Participant depending on where the Enquiry by Secondary Id was initiated from:
- If initiated as a stand-alone enquiry, customers can perform a Transfer Bank for proxies registered with other participants.
- If initiated from NAD - Deregistration, Suspend/Activate, or Modification, customers will only be able to view those proxies.
Main Drivers for the Introduction and Adoption of Secondary Identifiers
With secondary identifiers, beneficiaries can receive payments without sharing bank account details, enhancing privacy and reducing friction. Providing less sensitive information, like a phone number, is more convenient and less error-prone than typing an account number. This simplification improves the customer experience and promotes rapid adoption of secondary identifiers. The value of these proxy services depends on the number of registered participants, with business models being developed around fee-based schemes.
Proxy Types of Malaysia Domestic Scheme
Mobile Number Checksum
Enquiry with Secondary ID (620) with mobile number as the proxy.
During a Secondary ID enquiry, the response may include a list of masked mobile numbers, with only the last four digits exposed to assist in customer identification. However, in certain scenarios, comparing only the last four digits is insufficient for a reliable match and may lead to incorrect validation.
To address this, a mobile number checksum mechanism has been introduced. Participants are required to apply the checksum logic provided below to perform the necessary comparison. This allows participants to validate the full mobile number without exposing it, thereby improving accuracy while ensuring compliance with data privacy requirements.
How is the checksum calculated?
The check sum is calculated using a weight sum formula using Prime Numbers as its weight factor.
The checksum for Mobile Number +60104940395 is 731.
- Remove the leading plus sign ("+") from the mobile number:
+60104940395 → 60104940395 - Assign weight factors using consecutive prime numbers:
2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29 31 37 .. - Multiply each digit of the mobile number with its corresponding weight factor:
(6x2) + (0x3) + (1x5) + (0x7) + (4x11) + (9x13) + (4x17) + (0x19) + (3x23) + (9x29) + (5x31) - Add the products together to obtain the checksum, which is 731.